Gas, often known as flatulence or bloating, is a common digestive issue that affects many individuals worldwide. While occasional gas is normal, persistent or excessive gas can be uncomfortable and may indicate underlying health issues. Understanding the symptoms of gas can help you manage and alleviate this condition effectively.
Symptoms of Gas
Gas symptoms can vary from person to person but commonly include:
- Excessive Burping: Burping more frequently than usual, often accompanied by a noticeable sound or odor.
- Passing Gas: Increased frequency of passing gas through the rectum, sometimes with a strong or foul smell.
- Abdominal Bloating: Feeling of fullness, tightness, or swelling in the abdomen.
- Abdominal Pain: Sharp or cramp-like pains in the abdomen, often relieved by passing gas or a bowel movement.
- Discomfort: General discomfort or unease in the abdominal area, especially after eating or drinking.
Causes of Gas
Understanding the causes of gas can help identify triggers and manage symptoms effectively. Common causes include:
- Swallowed Air: Consuming food or drinks too quickly, chewing gum, or smoking can lead to excess air in the digestive tract.
- Dietary Factors: Certain foods and beverages can contribute to gas production, such as:
- High-Fiber Foods: Beans, lentils, broccoli, and whole grains contain complex carbohydrates that can be difficult to digest, leading to gas production.
- Carbonated Drinks: Soda and sparkling water release carbon dioxide gas, which can accumulate in the digestive system.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Sorbitol and mannitol found in sugar-free candies and gums can cause gas in some individuals.
- Digestive Disorders: Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), lactose intolerance, and celiac disease can impair digestion and lead to gas formation.
- Bacterial Imbalance: Changes in the gut microbiota, such as bacterial overgrowth or imbalance, can ferment undigested food particles and produce gases like hydrogen and methane.
- Medications: Some medications, including antibiotics and fiber supplements, can cause gas as a side effect by altering digestive processes.
Managing Gas Symptoms
Here are some guidelines on managing gas symptoms at home before considering consulting a healthcare professional:
- Slow down while eating: Eating or drinking too quickly can cause you to swallow air, leading to gas. Take your time to chew food thoroughly and avoid gulping down beverages.
- Identify trigger foods: Keep a food diary to identify foods that tend to trigger gas symptoms for you. Common culprits include beans, lentils, broccoli, cabbage, onions, and carbonated drinks. Limiting or avoiding these foods may help reduce gas.
- Consider dietary modifications: If you suspect certain carbohydrates are causing gas, consider following a low-FODMAP diet. This involves temporarily eliminating high-FODMAP foods and gradually reintroducing them to identify specific triggers. It’s best to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes.
- Be mindful of food intolerances: Intolerances to lactose or fructose can contribute to gas symptoms. If you suspect an intolerance, try eliminating the problematic food or drink from your diet and observe if the symptoms improve. Consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
- Probiotics: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help improve gut health. Consider incorporating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt or taking a probiotic supplement after consulting with a healthcare professional.
- Stay physically active: Regular exercise can aid digestion and prevent gas buildup. Engage in activities such as walking, jogging, or yoga to promote healthy digestion.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water throughout the day can help keep digestion smooth and prevent constipation, which can contribute to gas. Aim to drink an adequate amount of water daily.
- Avoid tight-fitting clothing: Wearing tight-fitting clothing can put pressure on the abdomen, contributing to gas discomfort. Opt for loose and comfortable clothing to alleviate any unnecessary pressure.
Remember, while these guidelines may provide relief for occasional gas symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if gas symptoms persist, worsen, or are accompanied by concerning symptoms. A healthcare professional can provide personalized advice and further evaluation if needed.
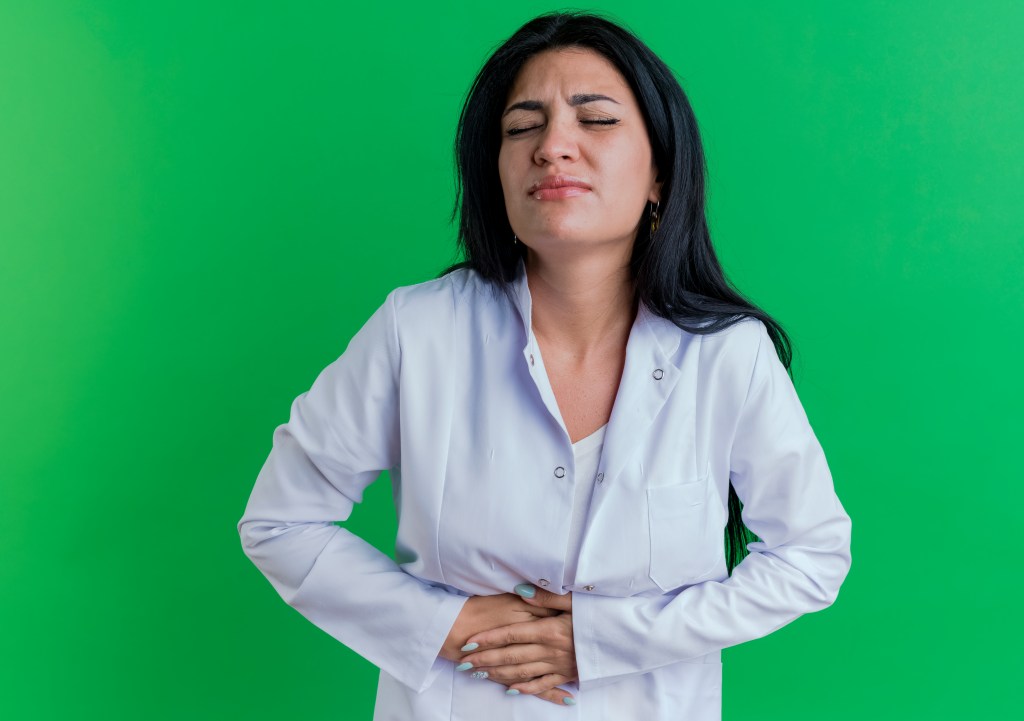

When to Seek Medical Advice
While occasional gas is normal, persistent or severe symptoms may indicate an underlying digestive disorder or medical condition. Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Severe or Prolonged Pain: Persistent abdominal pain that does not improve with passing gas or a bowel movement.
- Significant Changes in Bowel Habits: Sudden changes in stool frequency, consistency, or color.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Weight loss without dieting or exercise changes.
- Blood in Stool: Red or black stools may indicate bleeding in the digestive tract.
Conclusion
Gas is a common digestive issue that can be managed effectively with dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and, if necessary, medical intervention. By understanding the symptoms and causes of gas, individuals can take proactive steps to improve digestive health and reduce discomfort. Remember, each person’s digestive system is unique, so finding the right balance of diet and habits that work for you is key to managing gas symptoms effectively.
















Leave a comment