Acidity is a condition characterized by an excess production of acid in the stomach, leading to symptoms like heartburn, stomach pain, and regurgitation of acid. It is caused by factors such as an unhealthy diet, stress, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions. As for the number of people suffering from acidity, it is challenging to provide an exact figure as it varies across different populations and regions. However, it is a common issue globally, affecting a significant number of individuals. Factors such as dietary habits, lifestyle choices, and genetic predisposition can contribute to the prevalence of acidity. If you suspect you are experiencing acidity or related symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific condition and help manage the symptoms effectively.
These different types of acidity can vary in terms of severity, symptoms, and potential complications. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment based on the specific type of acidity one may be experiencing.
Technical Root Causes of Acidity:
- Excessive Gastric Acid Production: Acidity often arises due to an overproduction of gastric acid in the stomach. This can be triggered by numerous factors, including stress, certain medications, and an unhealthy diet.
- Weak or Inefficient Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES): The LES is a muscular valve that separates the esophagus from the stomach. When it becomes weak or relaxed, it allows stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, leading to acid reflux and heartburn.
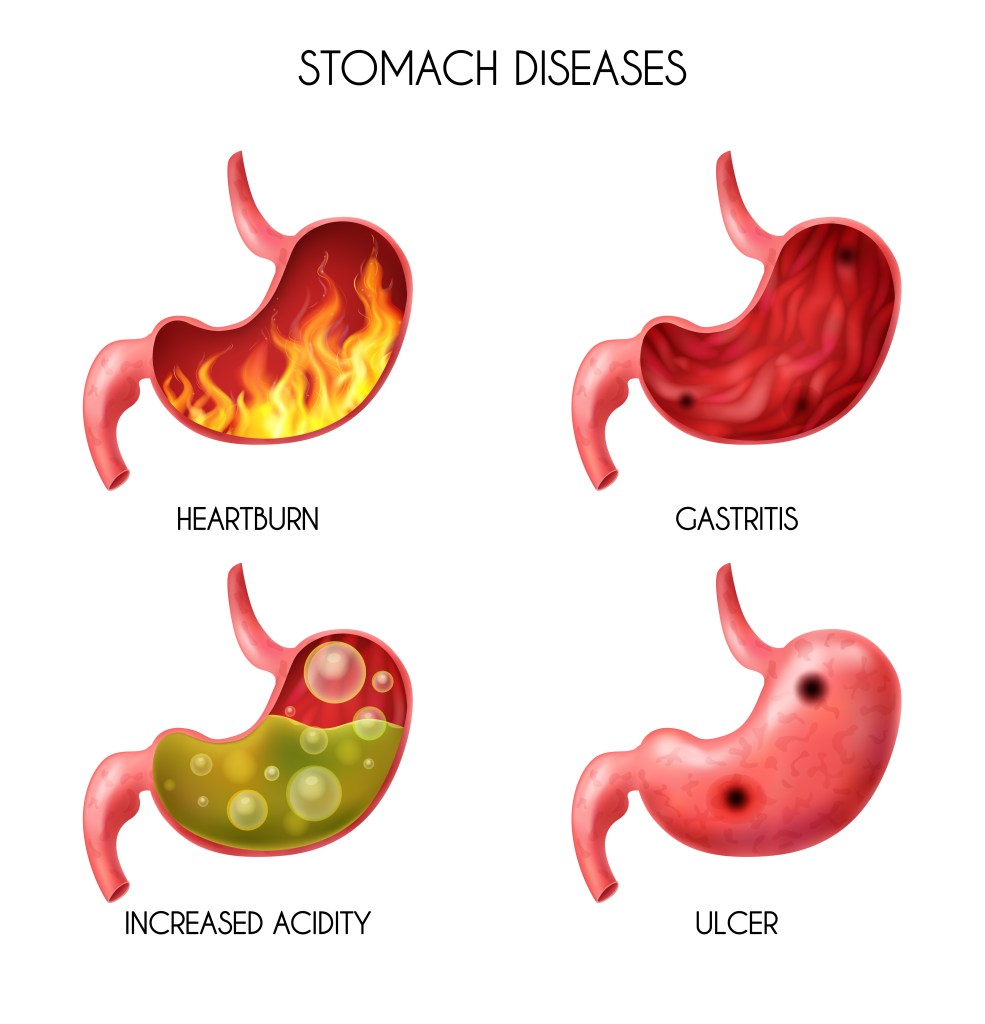
Types of Acidity:
- Gastric Acidity: This type of acidity occurs when there is an excess production of acid in the stomach. It commonly results in symptoms like bloating, stomach pain, and nausea.
- Acid Reflux: Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), happens when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. It can cause heartburn, chest pain, and a sour taste in the mouth.
Prevention of Acidity:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Avoid spicy, fatty, and acidic foods that can trigger excessive acid production. Opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate acidity symptoms. Engage in stress-reducing activities like exercise, meditation, or hobbies to promote overall well-being.
- Avoid Triggering Substances: Certain substances like caffeine, alcohol, tobacco, and carbonated beverages can worsen acidity. Limit or avoid their consumption.
Consequences of Acidity:
Prolonged acidity can lead to various complications that can significantly impact an individual’s overall health. Here are some potential complications associated with long-term acidity:
- Esophageal Damage: The constant exposure of the esophagus to stomach acid can cause inflammation, irritation, and erosion of the esophageal lining. This can lead to conditions such as esophagitis, esophageal ulcers, and even Barrett’s esophagus, a precancerous condition.
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding: In severe cases, prolonged acidity can cause erosion or ulceration of the stomach or duodenal lining, leading to gastrointestinal bleeding. This can result in symptoms like black, tarry stools or vomiting blood, indicating the need for immediate medical attention.
- Strictures and Narrowing: Chronic acid reflux can cause the development of scar tissue in the esophagus, leading to the narrowing of the esophageal pathway. This can cause difficulty swallowing, a sensation of food getting stuck, and the need for medical intervention to alleviate the narrowing.
- Dental Problems: The repeated exposure of tooth enamel to stomach acid can result in dental erosion, tooth sensitivity, and an increased risk of cavities. This can lead to tooth decay, tooth loss, and the need for dental treatments to restore oral health.
- Respiratory Issues: Acid reflux can trigger respiratory symptoms, such as chronic coughing, wheezing, and asthma-like symptoms. The inhalation of stomach acid into the lungs can cause irritation, inflammation, and potential respiratory infections.
- Sleep Disturbances: Acid reflux and heartburn can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to sleep disturbances and daytime fatigue. Continuous sleep deprivation can negatively impact overall health and well-being.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Acidity can affect the absorption of nutrients, particularly minerals like calcium, magnesium, and iron. Prolonged deficiencies in these essential nutrients can result in weakened bones (osteoporosis), anemia, and other health complications.
It is important to note that the severity and frequency of complications can vary among individuals and depend on various factors such as the underlying cause of acidity, lifestyle habits, and overall health. If you experience persistent or severe acidity symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis, treatment, and management.
Managing acidity through lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, medication, and addressing underlying health conditions can help prevent complications and promote overall well-being. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider can ensure appropriate monitoring and management of acidity-related complications, thus safeguarding an individual’s overall health.

Conclusion:
Acidity is a prevalent condition that can significantly impact the quality of life for individuals experiencing it. Understanding the technical root causes, different types of acidity, and taking preventive measures can help manage and alleviate symptoms. It is essential to address acidity promptly to prevent potential complications. If you are experiencing persistent acidity, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Remember, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eating a balanced diet, managing stress, and avoiding triggering substances can go a long way in preventing and managing acidity effectively. Take charge of your digestive health and prioritize your well-being.
















Leave a comment